LIDAR
back ground
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that measures distances by emitting laser pulses and analyzing the reflected signals. By calculating the time it takes for the laser light to return to the sensor, LiDAR can create highly accurate 3D representations of the surrounding environment.
LiDAR systems are widely used in various fields, including autonomous vehicles, robotics, mapping, and environmental monitoring. In robotics and SLAM applications, LiDAR plays a crucial role in enabling precise localization and real-time obstacle detection, even in low-light or textureless conditions. Its high spatial accuracy and reliability make it an essential sensor for advanced perception and navigation systems.
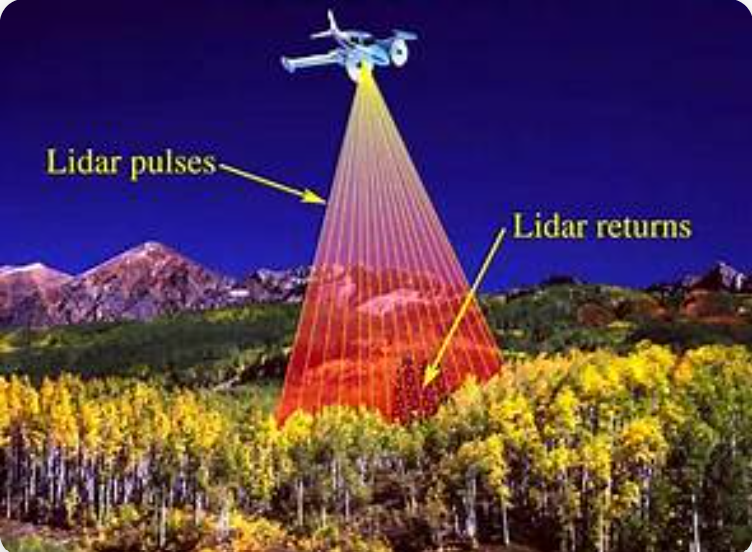




In conclusion, LiDAR has become one of the most reliable and precise sensing technologies for 3D environment perception. By using laser-based distance measurements, it provides detailed spatial information that is essential for accurate mapping, navigation, and object detection. Its high resolution and independence from lighting conditions make it superior to many traditional vision-based systems in certain scenarios.

Furthermore, as LiDAR technology continues to evolve, sensors are becoming smaller, faster, and more affordable. These advancements are expanding its applications beyond autonomous vehicles to include robotics, smart cities, and industrial automation. Overall, LiDAR plays a vital role in shaping the future of intelligent systems and real-time spatial understanding.